ABSTRACT
India accounts for one in every four tuberculosis (TB) cases around the globe. The fact that TB is easily transmitted to people with pre-existing conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, and lung impairment, among other immunity deteriorating factors, is concerning in contemporary times. As India leaps to overcome the USA and become the nation most infected with Covid-19, the risk to current TB patients could rise exponentially. Moreover, the susceptibility to and treatment of Covid-19 among TB patients could both be impacted negatively, leading to a possible nullification of the progress towards eliminating TB in India by 2025. In this context, this paper evaluates the worsening state of the TB epidemic in India’s battle against Covid-19.
THE FACE OF TUBERCULOSIS IN INDIA
TB is an airborne disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (MTB). It usually affects the lungs but may affect other parts of the body too. Despite being curable and preventable, the World Health Organization (WHO) has observed TB to be among the top
10 causes of death worldwide. In fact, about 25% of the world population is infected by MTB and is thus at risk of contracting TB (The Global Tuberculosis Report 2019).
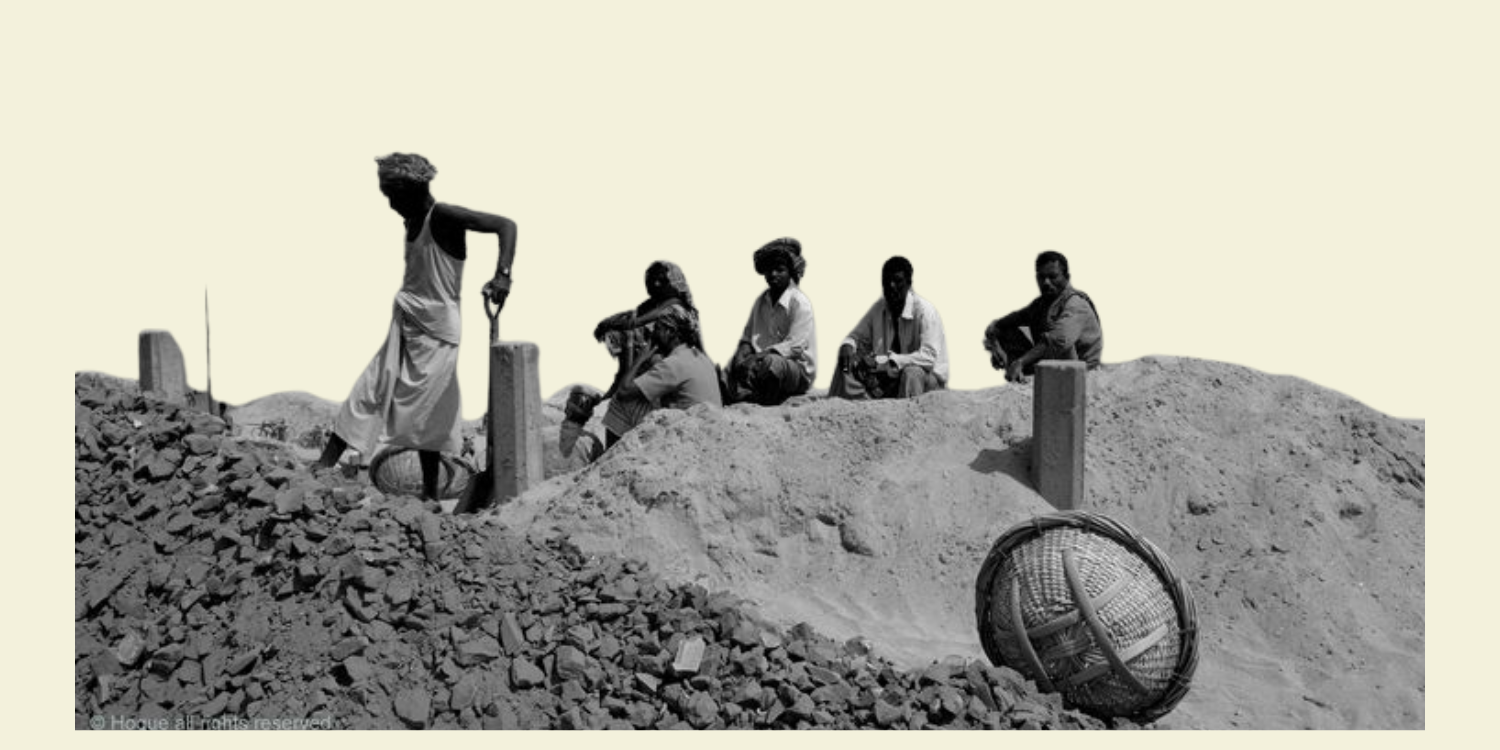
The TB epidemic has been a significant public health issue in India for a long time. India bears the highest burden of this disease in the world, with about 2.4 million cases reported every year or about 6,575 cases every day (India TB Report 2020). The incidence of the multidrug-resistant (MDR)11TB is also the highest in India with about one-quarter of the total cases (Chatterjee et al. 2018). With 79,000 deaths in 2019, India recorded the highest death toll due to TB in the world, totalling about 1,200 every day (India TB Report 2020).
Under-detection of TB cases is also a major problem in India due to a mix of poor access and incorrect diagnoses. The country “missed” the detection of about 56% of drug-resistant TB cases in 2018 and also missed three lakh such cases in absolute numbers in 2019 (WHO 2019; India TB Report 2020). Missing cases not only pose a disastrous risk of increased proliferation of TB but may also increase the chances of contracting drug-resistant forms of the disease.
With a share of 27% in the worldwide TB epidemic, India has been performing considerably worse than relatively poor economies (WHO 2019). As puzzling as the statistics may seem, India’s socio-economic conditions provide a hospitable environment for TB to proliferate. Being an airborne disease, TB expectedly thrives in overcrowded spaces with poor sanitation, inadequate ventilation, inefficient health infrastructure, and persistent malnutrition (Indian Medical Association 2015).